In the heart of urban jungles, a verdant oasis of houseplants thrives, bringing life, color, and a breath of fresh air to our indoor spaces. These silent witnesses to our daily routines have become indispensable companions, reminding us of our intrinsic connection to nature. Yet, the elixir of life that nourishes these leafy inhabitants, water, often holds untold secrets. The quality of this vital resource has a profound impact on the health and vitality of our botanical companions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the mysteries of water quality and its paramount role in houseplant health, transforming you into a true indoor gardener extraordinaire. We’ll explore the intricate dance between water quality factors and their impact on your houseplants, empowering you with the knowledge to create a thriving indoor garden that’s the envy of your friends and neighbors.
So, prepare to embark on an enlightening journey as we reveal the art and science of harnessing water quality to elevate your houseplants to new heights of growth and splendor!
The Basics of Water Quality
Water quality is a measure of the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water, which are influenced by a range of factors, such as pH level, hardness, salinity, dissolved oxygen, and the presence of contaminants.
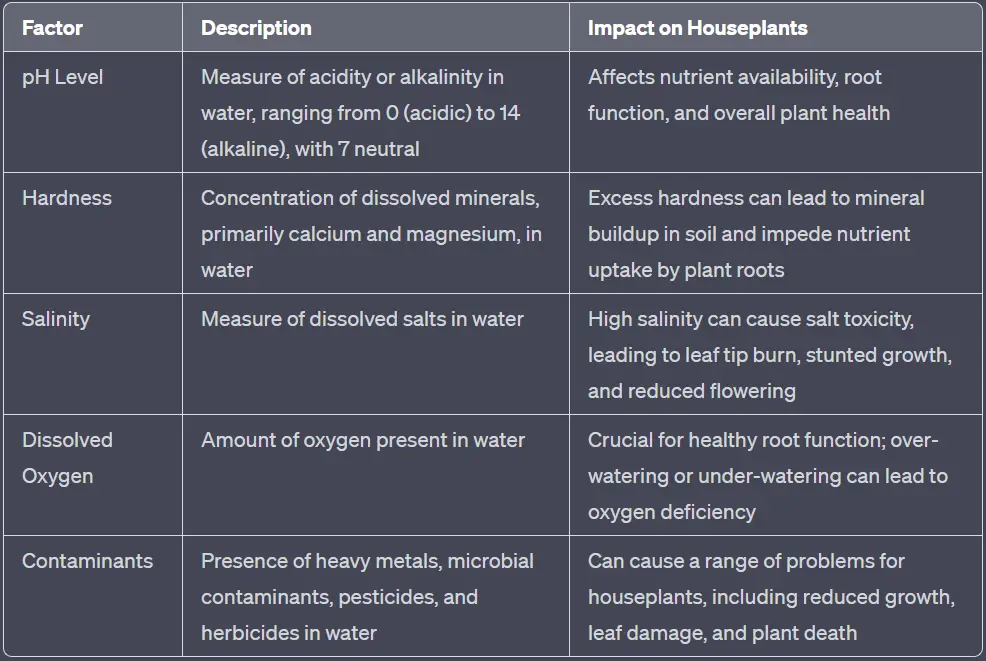
pH Level
The pH level of water is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Acidic water has a pH below 7, while alkaline water has a pH above 7. The pH level can have a direct impact on houseplant health, as it affects nutrient availability and root function.
Hardness
Water hardness refers to the concentration of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium, in the water. Hard water has high mineral content, while soft water has low mineral content. Excessively hard water can lead to the buildup of mineral deposits in the soil, which may impede nutrient uptake by houseplant roots.
Salinity
Salinity is the measure of dissolved salts in water. High salinity can negatively affect houseplants by causing salt toxicity, which can manifest as leaf tip burn, stunted growth, or even plant death. Some houseplants, however, are more tolerant of salt and can thrive in slightly saline conditions.
Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved oxygen is the amount of oxygen present in water, which is crucial for healthy root function. Over-watering or under-watering can lead to oxygen deficiency in the root zone, leading to root rot and other health problems in houseplants.
Contaminants
Various contaminants can affect water quality, such as heavy metals, microbial contaminants, pesticides, and herbicides. These contaminants can cause a range of problems for houseplants, including reduced growth, leaf damage, and even plant death.
The Impact of Water Quality on Houseplant Growth and Development
Water quality can have a profound impact on several aspects of houseplant health, including:
- Root system health: Oxygen availability and nutrient uptake are both influenced by water quality. Poor water quality can lead to weak, underdeveloped root systems that are more susceptible to disease and stress.
- Photosynthesis and respiration: Optimal water quality ensures efficient chlorophyll production and carbon dioxide uptake, both of which are essential for photosynthesis and respiration processes in houseplants.
- Cell division and elongation: Osmotic regulation and hormonal balance in houseplants are influenced by water quality. Poor water quality can lead to irregular cell growth and stunted development.
- Flowering and fruiting: Pollination, seed production, and overall reproductive success of houseplants can be affected by water quality.
Common Houseplant Issues Related to Poor Water Quality
Several issues can arise in houseplants due to poor water quality, including:
- Chlorosis: Yellowing of leaves due to a lack of chlorophyll production, often caused by pH imbalances or nutrient deficiencies.
- Leaf tip burn: Browning or scorching of leaf tips, typically caused by high salinity or the presence of contaminants in the water.
- Root rot: Decay of roots due to a lack of oxygen or the presence of harmful microbes in the water.
- Stunted growth: Slow or halted growth in houseplants, often resulting from nutrient deficiencies or toxic substances in the water.
- Reduced flowering: Diminished or absent flowers in houseplants, often due to imbalances in pH, salinity, or the presence of contaminants affecting the reproductive processes.
Water Quality Parameters and Their Effects on Houseplants
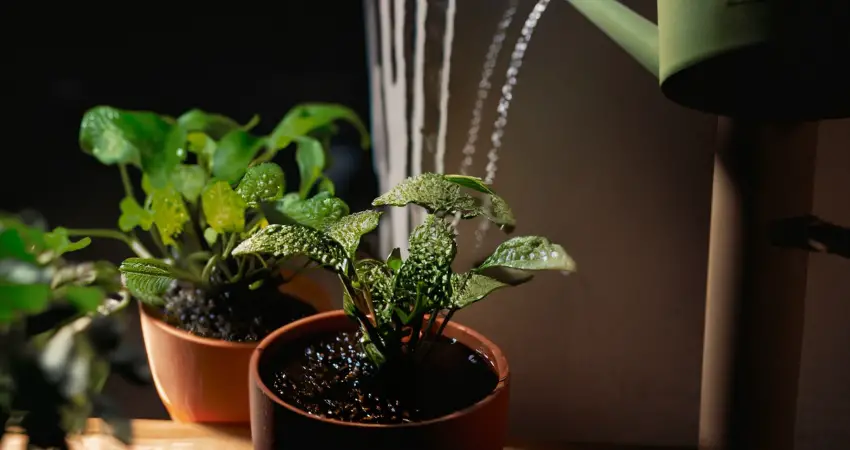

1. Effects of pH Level
Acidic Water
Acidic water can cause nutrient deficiencies in houseplants, as some nutrients become less available at lower pH levels. Additionally, acidic conditions may lead to the release of toxic elements, such as aluminum, which can cause harm to plants.
Alkaline Water
Alkaline water may also lead to nutrient deficiencies, as some essential nutrients become less available at higher pH levels. High alkalinity can also reduce the availability of micronutrients, such as iron and manganese, causing chlorosis and other growth problems.
Houseplant pH Preferences
Different houseplants have varying pH preferences. For instance, azaleas and gardenias prefer acidic conditions, while spider plants and snake plants grow better in slightly alkaline environments. It is essential to be aware of the specific pH preferences of your houseplants to ensure optimal growth.
2. Effects of Hardness
Effects of Hard Water on Plants
Hard water can cause a buildup of calcium and magnesium salts in the soil, leading to reduced nutrient uptake and potential plant stress. High mineral content in hard water can also lead to unsightly white deposits on leaves and pots, known as lime scale.
Soft Water and Plant Health
Soft water is generally more suitable for houseplants, as it does not cause mineral buildup in the soil. However, it may be deficient in some essential nutrients, such as calcium and magnesium, which may need to be supplemented through fertilizers.
3. Effects of Salinity
Salt Toxicity
High salinity can cause salt toxicity in houseplants, leading to symptoms such as leaf tip burn, stunted growth, and reduced flowering. In severe cases, salt toxicity can cause plant death.
Salt-tolerant Houseplants
Some houseplants, such as spider plants and snake plants, are more tolerant of saline conditions and can thrive even in moderately salty environments. However, it is still essential to monitor the salinity levels in your water and adjust them as needed to maintain optimal houseplant health.
4. Effects of Dissolved Oxygen
Over-watering
Over-watering can lead to oxygen deficiency in the root zone, as excess water displaces the air in the soil. This can result in root rot and other health issues in houseplants.
Under-watering
Under-watering can also cause oxygen deficiency, as dry soil may not be able to hold adequate amounts of water and oxygen for healthy root function. Regular monitoring of soil moisture levels is crucial to maintain a proper balance and ensure optimal houseplant health.
5. Effects of Contaminants
Heavy Metals
Heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium, and mercury, can be toxic to houseplants, leading to reduced growth, leaf damage, and even plant death. It is essential to ensure that the water you use for your houseplants is free of harmful heavy metals.
Microbial Contaminants
Microbial contaminants, such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses, can cause a range of diseases in houseplants, including root rot, leaf spots, and wilts. Ensuring that your water is free of harmful microbes is crucial for maintaining healthy houseplants.
Pesticides and Herbicides
Pesticides and herbicides can contaminate water sources and cause harm to houseplants if present in high concentrations. These chemicals can lead to a range of health issues, from reduced growth to plant death. Make sure to use clean, uncontaminated water for your houseplants.
Improving Water Quality for Houseplants
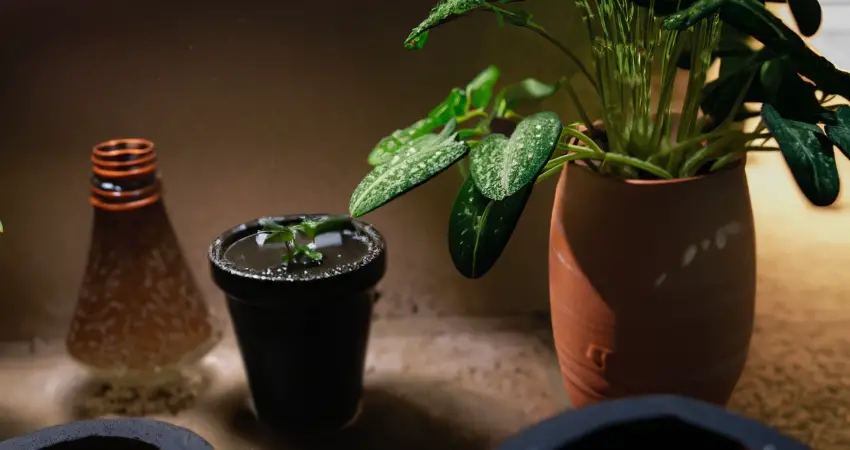

Water Treatment Methods
There are several methods to improve water quality for houseplants:
- Filtration: Using a water filtration system can help remove impurities, contaminants, and excess minerals from your tap water, making it more suitable for houseplants.
- Reverse osmosis: This process removes dissolved salts, contaminants, and heavy metals from water, resulting in high-quality water ideal for houseplants.
- Distillation: Distilled water is produced by boiling water and collecting the purified vapor, which is free of contaminants and minerals. This type of water can be beneficial for sensitive houseplants.
Rainwater Collection and Use
Rainwater is an excellent source of pure, soft water for houseplants. By collecting rainwater, you can provide your plants with natural, contaminant-free water that is rich in essential nutrients. Be sure to store collected rainwater in a clean container and use it within a reasonable time to avoid contamination.
Water Conditioners and Additives
Water conditioners and additives can help adjust the pH, hardness, and salinity levels of your water, making it more suitable for houseplants. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using these products to ensure the correct dosage and application.
Proper Watering Techniques
Implementing proper watering techniques can help maintain optimal water quality for your houseplants:
- Watering frequency: Be sure to water your houseplants according to their specific needs, as over-watering or under-watering can lead to oxygen deficiency and other issues.
- Watering volume: Ensure that you provide enough water to saturate the root zone without causing waterlogging or excessive runoff.
- Water temperature: Use room-temperature water when watering your houseplants, as cold or hot water can shock the plant’s roots and cause damage.
Case Studies: Houseplants and Water Quality
Let’s explore the effects of water quality on specific houseplant species:
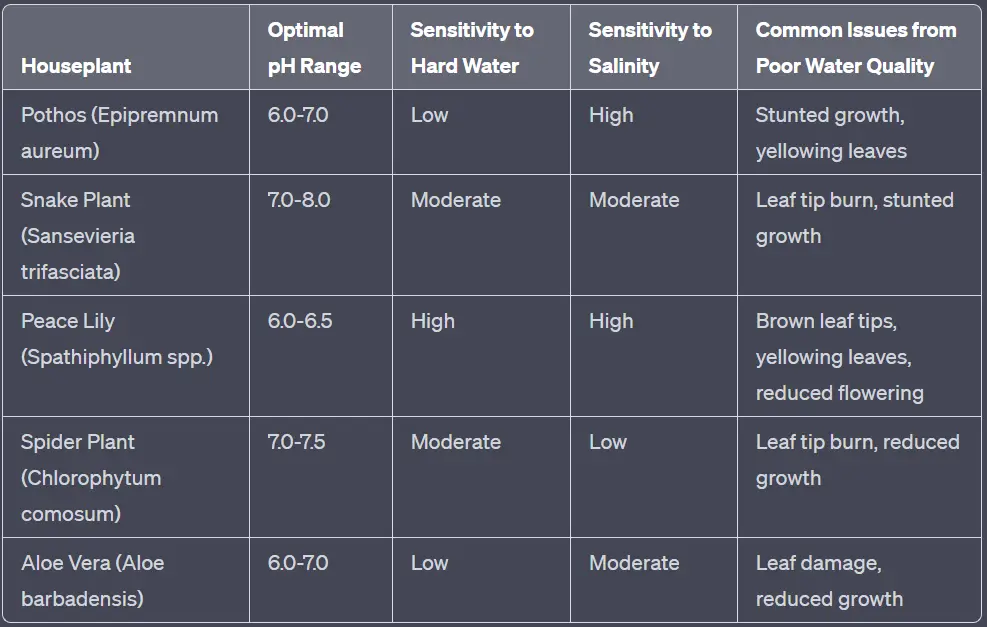
- Pothos (Epipremnum aureum): Pothos plants prefer slightly acidic to neutral water (pH 6.0-7.0) and are sensitive to high salinity levels. Poor water quality can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced overall health.
- Snake plant (Sansevieria trifasciata): Snake plants can tolerate a wide range of water conditions but thrive best in slightly alkaline water (pH 7.0-8.0). Excess salinity or contaminants in water can cause leaf tip burn and stunted growth.
- Peace lily (Spathiphyllum spp.): Peace lilies prefer slightly acidic water (pH 6.0-6.5) and are sensitive to hard water and high salinity. Poor water quality can result in brown leaf tips, yellowing leaves, and reduced flowering.
- Spider plant (Chlorophytum comosum): Spider plants can tolerate moderately hard water but prefer slightly alkaline conditions (pH 7.0-7.5). Poor water quality can cause leaf tip burn, reduced growth, and weak root systems.
- Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis): Aloe vera plants prefer slightly acidic water (pH 6.0-7.0) and are relatively tolerant of salinity. However, high levels of contaminants or heavy metals in water can cause leaf damage and reduced growth.
Water Quality Improvement and Houseplant Recovery
By improving the water quality and addressing the specific needs of each houseplant species, you can often see a significant recovery in plant health. This includes increased growth, improved leaf color, and enhanced flowering.
In conclusion, the significance of water quality in nurturing healthy, vibrant houseplants cannot be overstated. By delving into the various factors that affect water quality and their impact on your beloved green companions, you are now well-equipped to create a thriving indoor garden that radiates life and vitality. As you embark on your journey to master water quality, remember to consider the unique needs of each houseplant species and to monitor and adjust water parameters accordingly.
Embrace the power of water quality, and witness the extraordinary transformation in your lush, indoor haven. May your houseplants flourish and bask in the glory of optimal water quality, as you continue to nurture them with dedication and love.
